Vocal Cord Polyp
Polyps are fluid-filled tissue deformations that are formed on the tissues covered with mucosal structure in the body, develop by adhering to the tissue, resemble a tumour and are filled with fluid.
Untreated polyps can cause major and important health problems over time. They can be seen in many areas such as the nose, throat, vocal cords, intestines, gallbladder, and uterus. Although they are mostly benign, there are also malignant types that have the risk of becoming cancerous.
They are attached to the tissue on which they are formed, sometimes with a small stalk and sometimes with a broad base. They can be of very different sizes. They can heal on their own. As they increase in size, the severity of the complaints they cause increases and they are surgically removed.
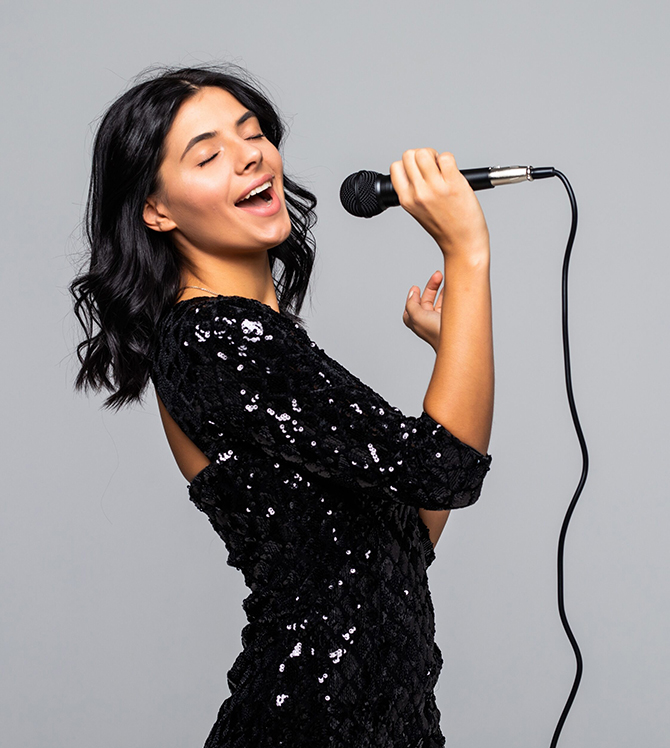
Vocal Cord Polyp (Vocal Cord Polyp) is a fluid-filled, benign tissue deterioration that prevents the closure of the vocal cords, usually caused by intra-tissue haemorrhages in the middle part of the free surface where the vocal cords come into contact with each other. Like nodules, it can occur as a result of long-term use of the voice at the wrong intensity and loudness (pitch) or excessive use of the voice, or it can be seen after a single voice strain. Unlike nodules, it may occur in one or both vocal cords. Its appearance is distinctly red in colour. It contains numerous blood vessels and progresses towards a vascularised structure. They come in different shapes and sizes, but are often larger than nodules and resemble blisters.
Reinke’s Oedema (Polypoid Degeneration), which can be seen in all individuals but is more common in women and manifests itself with a thick voice, is a different type of vocal cord polyp. Excessive smoking is the biggest factor in its formation.
How is Vocal Cord Polyp Surgery Performed?
After the diagnosis of vocal cord polyp is made, if the voice rest, drug treatment and voice therapy methods applied to the patient do not yield results, a decision for surgical intervention is made. Endoscopic methods called Phonomicrosurgery and Microlaryngoscopy, which do not involve any external incision, are used:
Untreated polyps can cause major and important health problems over time. They can be seen in many areas such as the nose, throat, vocal cords, intestines, gallbladder, and uterus. Although they are mostly benign, there are also malignant types that have the risk of becoming cancerous.
Since the reason for the formation of vocal cord polyps is the wrong behaviour in the use of the voice, it is strongly recommended to receive voice therapy to prevent recurrence after the vocal cords have healed.
What are the Symptoms of Vocal Cord Polyps?
Although the symptoms vary in each individual, vocal cord polyps should be suspected when the following symptoms are seen alone or together:
- Lowering the Volume,
- Forking,
- Voice changes seen in the form of trembling,
- Changes in Voice Tone During Speech,
- Deterioration of Sound Quality,
- Restlessness and Pain in the Throat,
- Neck Pain
If the vocal cord polyps are not diagnosed and diagnosed and the necessary treatment is not applied, it may cause irreparable problems such as scar formation on the vocal cord (scar), painful voice use, permanent hoarseness.
A detailed examination of the vocal cords should be performed by a specialist ear-nose-throat doctor to determine whether the complaints are caused by vocal cord polyps.





 Türkçe
Türkçe РУССКИЙ
РУССКИЙ Spanish
Spanish Français
Français
